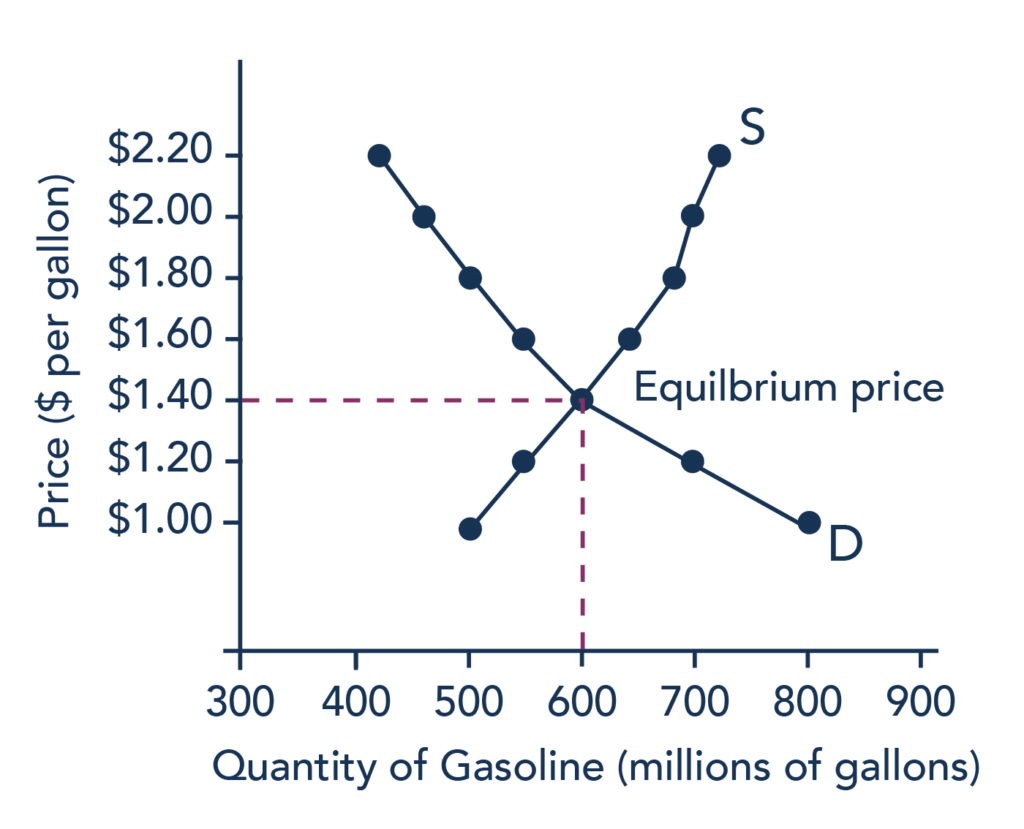
Production Cost Equilibrium . Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web there are two approaches to arrive at the producer’s equilibrium: The goal of a firm is to produce the given.
from courses.lumenlearning.com
Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web there are two approaches to arrive at the producer’s equilibrium: The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production.
Equilibrium, Price, and Quantity Introduction to Business
Production Cost Equilibrium Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web there are two approaches to arrive at the producer’s equilibrium:
From saylordotorg.github.io
Why Do Prices Change? Production Cost Equilibrium The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From www.intelligenteconomist.com
Supply And Demand Intelligent Economist Production Cost Equilibrium Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web there are two approaches to arrive at the producer’s equilibrium: Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT General Equilibrium PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID Production Cost Equilibrium The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From www.intelligenteconomist.com
Perfect Competition Short Run Intelligent Economist Production Cost Equilibrium Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From quizlet.com
Suppose the economy is in a longrun equilibrium. a. Draw a Quizlet Production Cost Equilibrium Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. The. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From analystprep.com
Factors Affecting LongRun Equilibrium Example CFA Level 1 AnalystPrep Production Cost Equilibrium Web there are two approaches to arrive at the producer’s equilibrium: Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. The goal of a firm is to produce. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From saylordotorg.github.io
Demand, Supply, and Equilibrium Production Cost Equilibrium Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From www.chegg.com
Solved Consider the market shown in equilibrium at point A Production Cost Equilibrium Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web there are two approaches to arrive at the producer’s equilibrium: Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces,. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From keplarllp.com
😀 Explain equilibrium price. Supply and Demand The Market Mechanism Production Cost Equilibrium The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From lasopadelta877.weebly.com
Marginal cost and supply curve lasopadelta Production Cost Equilibrium Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From conspecte.com
The Law of Supply and the Supply Curve Production Cost Equilibrium Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web there are two approaches to arrive at the producer’s equilibrium: Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From saylordotorg.github.io
Supply and Demand Production Cost Equilibrium The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From passnownow.com
SS1 Economics Third Term Equilibrium Price/Price Determination Production Cost Equilibrium Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From saylordotorg.github.io
Using the SupplyandDemand Framework Production Cost Equilibrium Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue (mr) and marginal cost (mc) of production. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. Web. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From www.shareyouressays.com
How is Equilibrium Price determined in a Market? Explained! Production Cost Equilibrium Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From studylib.net
Lecture 17 General Equilibrium Production Economy (part I Production Cost Equilibrium The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web this optimum level of production, also called producer’s equilibrium, is achieved when maximum output is derived from. Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained in terms of marginal revenue. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The graphs below illustrate an initial equilibrium Production Cost Equilibrium Web there are two approaches to arrive at the producer’s equilibrium: Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web as a result, producer equilibrium is determined by considering the costs of both labour and capital. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand,. Production Cost Equilibrium.
From www.chegg.com
Solved The market equilibrium quantity is (1.5, 2, 2.5, Production Cost Equilibrium Web determine the equilibrium price, what each frm produces, the total quantity, and the number of frms • graph how factor. Web when the price is below equilibrium, there is excess demand, or a shortage —that is, at the given price the quantity demanded,. The goal of a firm is to produce the given. Web producer’s equilibrium is often explained. Production Cost Equilibrium.